Avian Influenza Overview

Yo, what’s up, bird lovers! Let’s dive into the world of avian influenza, also known as bird flu. It’s a viral infection that can spread like wildfire through poultry flocks, causing major headaches for farmers and potentially posing a threat to humans too.
Avian influenza has been a hot topic lately, and I’m sure many of you are wondering what the fuss is all about. Well, let me tell you, it’s a serious issue that could potentially have a major impact on our food supply.
And speaking of major impacts, have you heard about the Bobby Witt Jr. contract ? It’s a massive deal that could shake up the MLB landscape. But back to avian influenza, it’s important to stay informed about this issue and take precautions to protect your flocks.
Avian influenza viruses come in various strains, each with its own quirks. Some strains are highly pathogenic, meaning they can cause severe illness and death in birds. Others are low pathogenic, causing milder symptoms or even going unnoticed. But even the low pathogenic strains can still have a significant economic impact on the poultry industry.
Global Distribution and Prevalence
Bird flu is a global issue, affecting poultry flocks in countries all over the world. The virus can spread through contact with infected birds or their bodily fluids, or through contaminated food, water, or equipment. Wild birds, especially migratory waterfowl, can also play a role in spreading the virus.
Avian Influenza Transmission and Prevention

Avian influenza is a contagious viral infection that affects birds, especially poultry. It can spread quickly through direct or indirect contact with infected birds or their bodily fluids, and can also be transmitted through contaminated environments.
Preventing the spread of avian influenza is crucial to protect both poultry populations and human health. Several measures are employed to control the disease, including surveillance, biosecurity, and vaccination.
Transmission Routes, Avian influenza
Avian influenza can spread through various routes:
- Direct Contact: Infected birds shed the virus in their saliva, nasal discharge, and feces. Direct contact with these fluids or infected birds can transmit the virus.
- Indirect Contact: The virus can survive on surfaces and objects for extended periods. Contact with contaminated equipment, clothing, or surfaces can lead to infection.
- Environmental Factors: The virus can be carried by wind and water, and can survive in soil and manure. Exposure to contaminated environments can increase the risk of infection.
Prevention Measures
To prevent the spread of avian influenza, several measures are implemented:
- Surveillance: Regular monitoring of poultry populations for signs of infection helps identify outbreaks early on and allows for prompt response.
- Biosecurity: Implementing strict biosecurity measures on poultry farms reduces the risk of exposure to the virus. This includes measures such as isolating poultry from wild birds, using protective clothing and equipment, and disinfecting premises regularly.
- Vaccination: Vaccinating poultry against avian influenza can help protect them from infection and reduce the severity of the disease if infected.
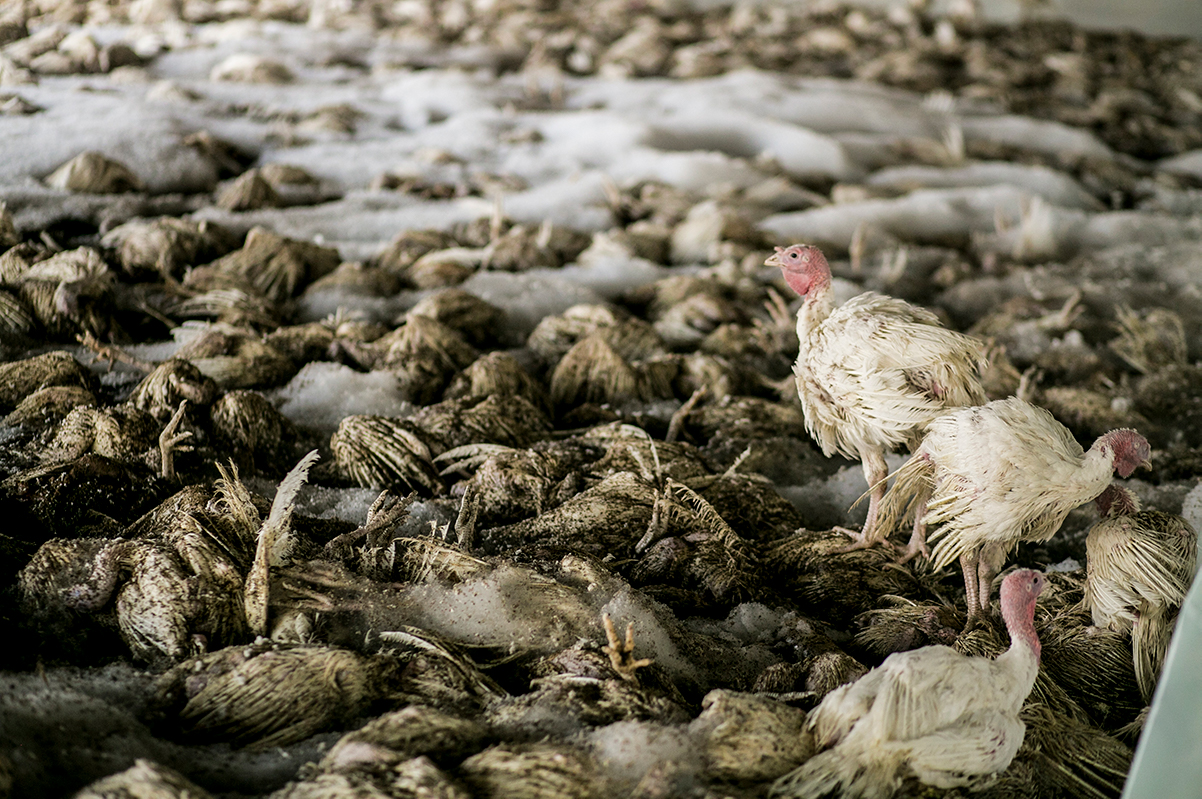
Avian Influenza Impact and Management
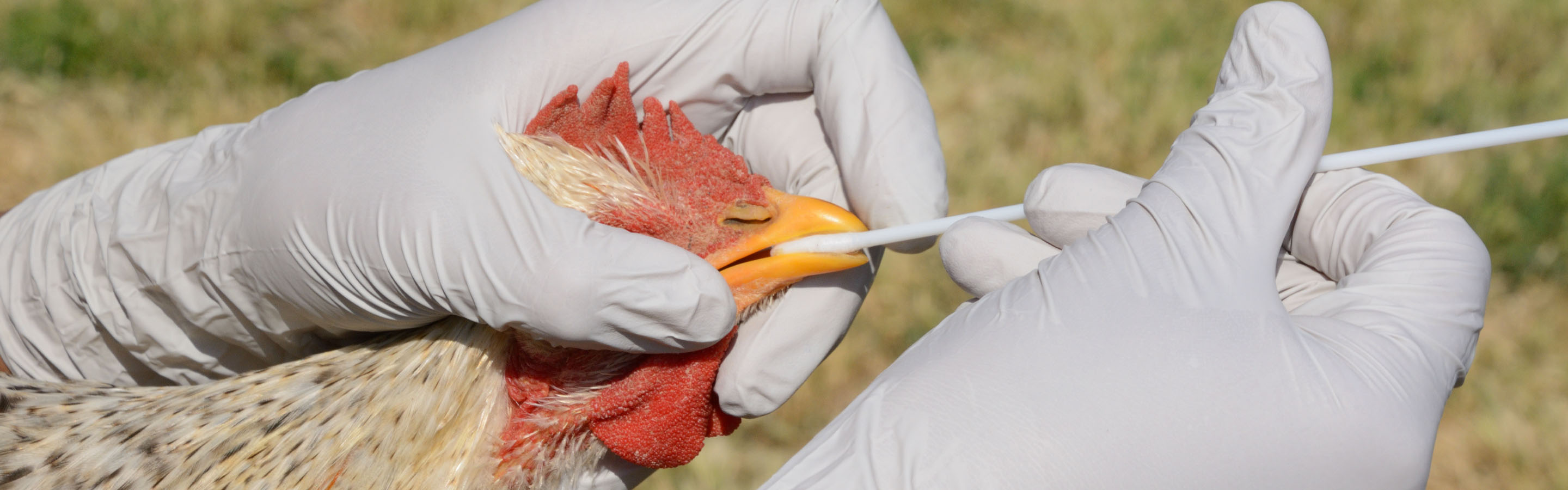
Avian influenza, also known as bird flu, is a highly contagious viral disease that can infect poultry and wild birds. Outbreaks of avian influenza can have significant economic and public health implications.
Economic Impact: Outbreaks of avian influenza can lead to significant economic losses for the poultry industry. Infected birds must be culled to prevent the spread of the disease, which can result in the loss of millions of birds and disruption of the poultry supply chain. Additionally, trade restrictions imposed by countries to prevent the spread of the virus can further impact the poultry industry.
Public Health Impact: While avian influenza primarily affects birds, some strains can also infect humans. Human infections with avian influenza can range from mild to severe, and in some cases, can be fatal. Outbreaks of avian influenza in humans can strain healthcare systems and lead to public health emergencies.
Strategies for Managing Avian Influenza Outbreaks
To manage and control avian influenza outbreaks, a combination of strategies is employed, including:
- Surveillance and Monitoring: Regular surveillance and monitoring of poultry and wild birds for signs of avian influenza is essential for early detection and containment of outbreaks.
- Biosecurity Measures: Implementing strict biosecurity measures on poultry farms and in the wild bird population can help prevent the spread of the virus. This includes measures such as isolation of infected birds, disinfection of premises, and movement restrictions.
- Vaccination: Vaccination of poultry can help reduce the severity of outbreaks and prevent the spread of the virus.
- Culling: In the event of an outbreak, infected birds must be culled to prevent further spread of the virus.
- International Cooperation: International cooperation and collaboration are crucial for mitigating the impact of avian influenza. This includes sharing information, coordinating surveillance efforts, and implementing joint prevention and control measures.
Guys, you know about avian influenza, right? It’s a nasty disease that affects birds, and it can be really dangerous. But here’s something interesting: did you know that Jhon Arias has been doing some amazing research on avian influenza? He’s a top scientist in the field, and he’s made some real breakthroughs.
So if you want to learn more about avian influenza, definitely check out his work.